Knee pain is a common ailment that affects people of all ages and lifestyles. Whether you’re an athlete pushing your body to its limits or an office worker spending hours at a desk, knee pain can significantly impact your quality of life.
However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, many knee conditions can be effectively managed, allowing individuals to regain functionality and alleviate pain. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of your knee pain and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Remember, early intervention and a comprehensive approach can make all the difference in your journey toward a pain-free and active lifestyle. In this blog,I will explore the various causes of knee pain and discuss effective treatments to help you find relief and regain mobility.
Anatomy of the knee
The knee is a vulnerable joint that bears a great deal of stress from everyday activities, such as lifting and kneeling, and from high-impact activities, such as jogging and aerobics.
The knee is formed by the following parts:
- Tibia. This is the shin bone or larger bone of the lower leg.
- Femur. This is the thighbone or upper leg bone.
- Patella. This is the kneecap.
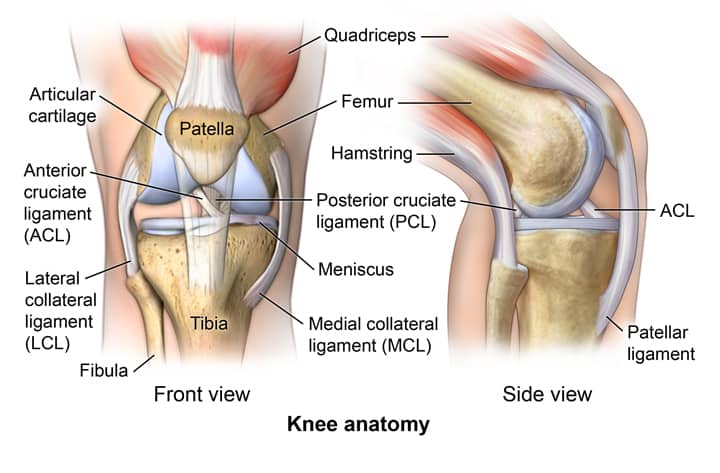
Each bone end is covered with a layer of cartilage that absorbs shock and protects the knee. Basically, the knee is 2 long leg bones held together by muscles, ligaments, and tendons.
There are 2 groups of muscles involved in the knee, including the quadriceps muscles (located on the front of the thighs), which straighten the legs, and the hamstring muscles (located on the back of the thighs), which bend the leg at the knee.
Tendons are tough cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones. Ligaments are elastic bands of tissue that connect bone to bone. Some ligaments on the knee provide stability and protection of the joints, while other ligaments limit forward and backward movement of the tibia (shin bone).
What are the symptoms when you injure your knee?
The location and severity of knee pain may vary, depending on the cause of the problem. Signs and symptoms that sometimes accompany knee pain include:
- Swelling and stiffness
- Redness and warmth to the touch
- Weakness or instability
- Popping or crunching noises
- Inability to fully straighten the knee
Most common types of knee injury
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent cause of knee pain, especially among older individuals. It occurs when the protective cartilage in the joints breaks down, resulting in bones rubbing against each other. Symptoms include stiffness, swelling, and pain during movement. Treatment options for osteoarthritis range from pain management medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications to assistive devices and, in severe cases, surgical intervention.
Ligament Injuries
Ligament injuries, such as a torn anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) or a sprained medial collateral ligament (MCL), are often associated with sports activities or sudden twists and turns. These injuries cause significant pain, swelling, instability, and difficulty with movement. Treatment for ligament injuries can involve rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE), physical therapy, bracing, and, in severe cases, surgical reconstruction.
Meniscus Tears
The meniscus is a cartilage cushion between the thigh bone and shin bone. Sudden twisting movements or degenerative changes can lead to meniscus tears, causing pain, swelling, and limited range of motion. Treatment options for meniscus tears include conservative management with rest, ice, and physical therapy, as well as surgical repair or removal, depending on the severity and location of the tear.
Tendinitis
Tendinitis, also known as tendonitis, is the inflammation of the tendons around the knee joint. It commonly affects athletes and individuals engaged in repetitive activities. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and tenderness around the affected tendon. Treatment for tendinitis typically involves rest, ice, physical therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and in some cases, corticosteroid injections.
Bursitis
Bursitis refers to the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the joints. Knee bursitis often occurs due to repetitive kneeling or direct trauma to the knee. Symptoms include pain, swelling, and warmth around the affected area. Treatment options for bursitis include rest, ice, compression, NSAIDs, and occasionally, aspiration of the bursa or corticosteroid injections.
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome (PFPS) is a condition characterized by pain in the front of the knee, specifically around the patella (kneecap). It commonly affects athletes, runners, and individuals with muscle imbalances. Treatment for PFPS involves physical therapy, strengthening exercises, activity modification, orthotics, and occasionally, bracing.
Fractures
The bones of the knee, including the kneecap (patella), can be broken during falls or auto accidents. Also, people whose bones have been weakened by osteoporosis can sometimes sustain a knee fracture simply by stepping wrong.
Hip or foot pain
If you have hip or foot pain, you may change the way you walk to spare your painful joint. But this altered gait can place more stress on your knee joint and cause knee pain.
Baker Cyst
A Baker’s cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling that develops at the back of the knee joint. The cyst forms when excess fluid accumulates in a small sac called the synovial bursa, which is present in the knee joint.
Baker’s cysts often develop as a result of underlying knee conditions such as arthritis, meniscal tears, or other injuries that cause inflammation and increased production of synovial fluid. The excess fluid then collects and bulges out at the back of the knee, creating a noticeable lump or swelling.
Sources:
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/knee-pain-and-problems
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/knee-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20350849
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/bakers-cyst-popliteal-cyst/